In actual processing, cutting stainless steel is often accompanied by the phenomenon of knife breaking and sticking. Because of the large plastic deformation of stainless steel in cutting, the chips produced are not easy to break and bond, which leads to severe hardening in cutting process. Hardening layer is produced in the next cutting process by each cutting tool. After layer accumulation, the hardness of stainless steel in cutting process is increasing, and the cutting force required is also increasing.
The generation of hardening layer and the increase of cutting force will inevitably lead to the increase of friction between tool and workpiece, and the increase of cutting temperature. Moreover, the thermal conductivity of stainless steel is small, the heat dissipation condition is poor, and a large amount of cutting heat is concentrated between the tool and the workpiece, which makes the machined surface worse and seriously affects the quality of the machined surface. Moreover, the increase of cutting temperature will aggravate tool wear, which will cause crescent depression on tool rake face and notch on cutting edge, thus affecting the surface quality of workpiece, reducing work efficiency and increasing production cost.

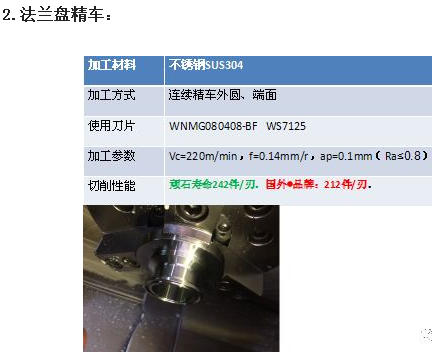



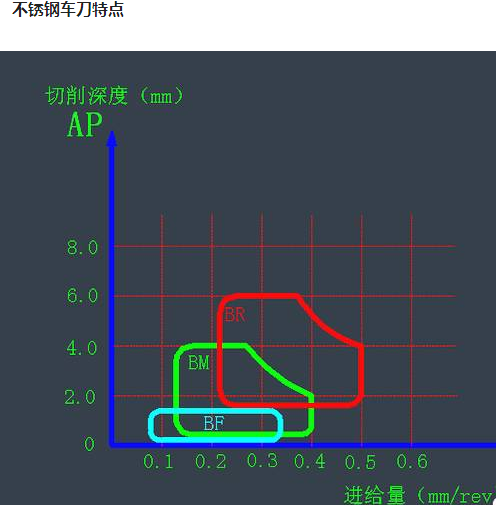

 中文
中文 English
English

